Maryland received more than $3.2 billion in Coronavirus Elementary and Secondary School Emergency Relief (ESSER) Fund dollars. Those resources were spread across the three, emergency federal pandemic recovery pieces of legislation:
Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security Act (CARES) - ESSER I
Coronavirus Response and Relief Supplemental Appropriations Act (CRRSA) - ESSER II
American Rescue Plan (ARP) Act - ESSER III
ARP Local Maintenance of Equity
All LEAs have been excepted from the FY 2022 Maintenance of Equity Requirement under section 2004(c)(2) of the American Rescue Plan (ARP) Act
All LEAs have been excepted from the FY 2023 Maintenance of Equity Requirement under section 2004(c)(2) of the American Rescue Plan (ARP) Act.
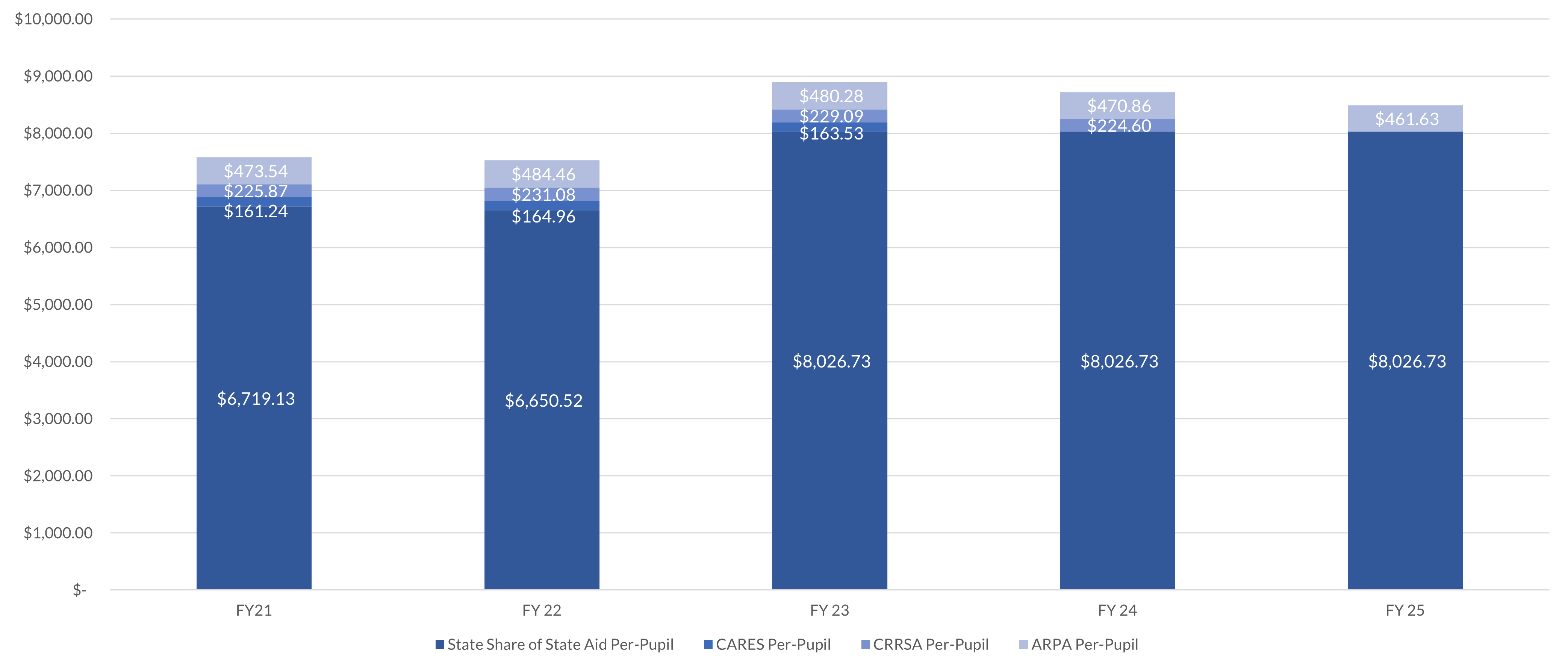
Maryland LEA ESSER Funding as a Portion of all K–12 State Aid
Maryland received more than $3 billion in ESSER funding for Maryland's schools. $3 billion constitutes a substantial, one-time infusion of federal funds into Maryland schools. However, those funds are spread across five school/fiscal years and are intended to serve the State's more than 860,000 children each year. In total, the aggregate amount of funding comes to less than $500, per-pupil for each tranche of Federal funding over the course of the funding term. What does that look like compared to the State Share of State Aid Maryland provides each year? In FY 2023, Maryland will provide, on average, $8,027, per-pupil in the State Share of State Aid to Maryland school districts, substantially more than the average ESSER per pupil. The proportion of LEA ESSER funds relative to State Aid is even smaller when counting the additional, local half of State Aid.
The Pace of ESSER Spending
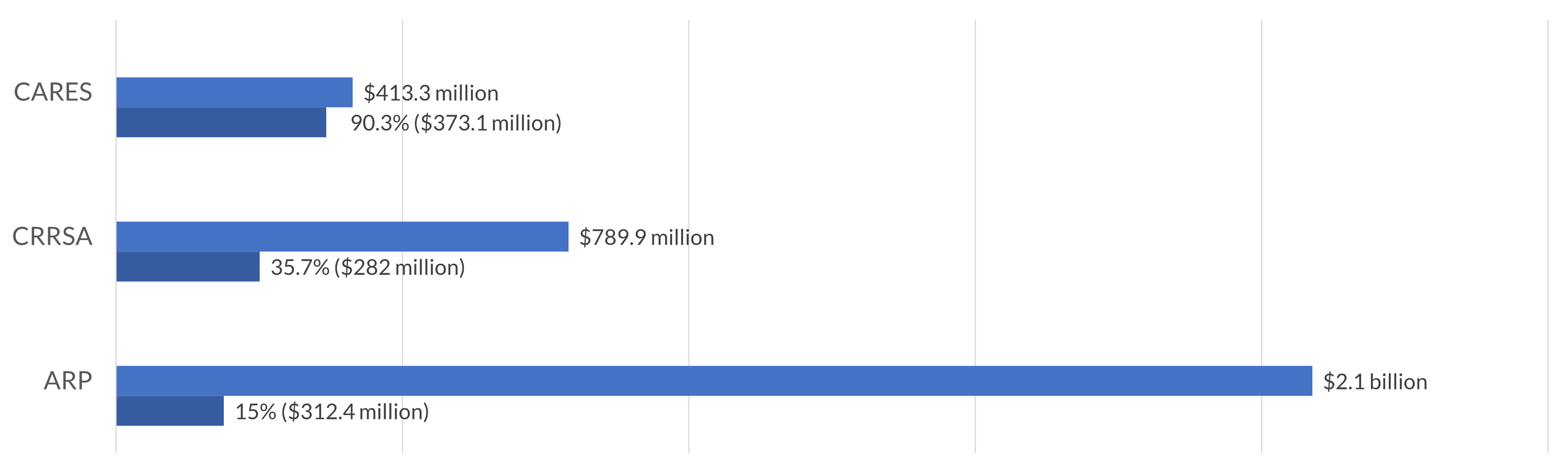
As of June 2022, Maryland LEAs are spending at the pace MSDE would expect given the order of the fund obligation and liquidation deadlines and the length of the grant performance period. “Districts are not spending fast enough” is not a trend observed in Maryland LEAs.

The appropriate spending pattern MSDE would expect as of June 2022 would be to see the majority of ESSER I funding reported as spent, some spending of total ESSER II funds, and little spending of ESSER III funds, given the timelines associated with obligating those grants (ESSER I, September 30, 2022; ESSER II, September 30, 2023; and ESSER II, September 30, 2024).
LEA ESSER Spending
Initial spending, State-wide, has focused on non-personnel costs related to PPE, planned HVAC investments, and hotspots/laptops. The largest personnel costs are stipends and extra pay for teachers who are providing tutoring interventions, extended day/summer learning, and for janitorial and custodial salaries. LEAs also used some ESSER resources to invest in Blueprint-related work (e.g., Blueprint Coordinator salaries).
Each link below directs to a page with the respective LEA's data. These data contain the ESSER spending amounts in dollars, to date as of February 2023. This means that the data may not include all ESSER spending. These data do not include encumbered local funds - only funds that are spent (transacted) and reported to MSDE for reimbursement in the Department's AFR system.
For the best user experience, view the data on a desktop device rather than a mobile device.
Examples of Spending, by Category
The above-provided data are grouped by spending category. Common examples of spending, within the various spending categories are:
Supplies and Materials
Equipment
Instructional Salaries and Wages
Extra duty salary pay for teachers and instructional staff to cover extended day tutoring or intervention services;
Extra duty salary pay for professional development and virtual course design
Special education teacher and paraprofessional salaries and stipends
Mental health staff support salaries
Stipends
Retention incentives for various staff members
Additional pay, akin to extra duty pay, for extended day support and academic interventions
Other Salaries
Contractual Services
Capital Outlay
Transportation
Resources
Download the source data excel file (Updated August 26, 2024)
Download the source data excel file (Updated January 30, 2023)
Download the source data excel file (Updated June 26, 2022)
Download the MSDE LEA ARP ESSER Monitoring Tool (Updated June 26, 2022)
Contact: